Panchakarma Treatment: Techniques, Benefits, and What to Expect
What is Panchakarma? The word Panchakarma came from the Sanskrit word Pancha means Five and Karma means Treatment. The prime objective of Panchakarma Therapies is to detoxify and purify the body.
This therapeutic measure is done for both healthy and unhealthy people. It helps an unhealthy person to get rid of various chronic diseases and helps the healthy person as a preventive treatment to keep the body physically and mentally fit.
Panchakarma Therapies have their importance in Ayurveda. In Charaka Samhita, an ancient Ayurvedic text author Aacharya Charak has very well described the extensive use of Panchakarma therapy for almost every major disease.
Two separate sections of Charak Samhita called Kalpa Sthanam and Siddhi Sthanam in which it has been describing the details of special decoctions and other preparations used for the Panchakarma therapy.
Panchakarma is a therapy to clean toxic materials from the body which is left by disease or due to poor nutrition. Our body can efficiently process and remove toxic materials, including the vitiated doshas.
It is due to one’s repeated dietary indiscretions, lifestyle, and poor exercise patterns the Agni so-called “digestive fire” which regulates our body’s internal homeostasis becomes ineffectual.
Other factors such as genetic predisposition, metabolic co-factors, and hormones can also lead to the accumulation of toxins that spread throughout the body resulting in disease. This particular waste material is called “Ama” in Ayurveda.
This Ama is a foul-smelling sticky and harmful substance that needs to be completely evacuated from the body if not it may invite many diseases. For this purpose, Panchakarma, the therapeutic measures of detoxification are needed.
What is the panchakarma process?
The panchakarma process includes 3 parts namely
- Poorva Karma
- Pradhan Karma
- Panchakarma
Besides this there are many subtypes of this therapy in which different types of massages are given such as herbal massages, external oil massage, and treatments with steam are also given.
These applications are very helpful in relieving deep-seated diseases as well as beneficial in maintaining and improving physical and mental health.
Panchakarma Charts
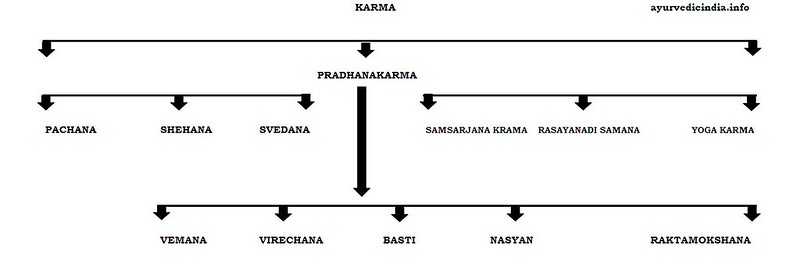
i). Poorva Karma (Pre Detox Measures) Which Includes
This cleansing and rejuvenating program is for the body, mind, and consciousness; it includes three main parts namely:
- Paachan (Digestion)
- Snehan (Internal and external oleation)
- Swedan (Fomentation)
1. Paachan (Digestion)
Stimulating digestive juices are agents that directly stimulate Biofire (Agni) it allows the undigested food to be processed without stimulating digestive enzymes.
The administration of digestants and stimulating digestive juice is a vital aim of Panchakarma treatment. Its objective is to improve both digestion at the cellular level and the gastrointestinal tract.
Normal digestion is achieved by the administration of medicated dehydrated butter (ghee) when it is mixed with digestive stimulants and digestive juices. Dehydrated butter is a powerful stimulating Biofire agent.
Some of the Commonly used digestants and digestive juice stimulants are Arka Vati, Agnitundi Vati, Panchakoladi churna, Hingwashtak churna, Pippalyadi ghrita, Dashmoolarishta.
Any of this preparation is generally administered for 3 to 7 days, depending on the person’s age, disease, and condition.
After that one can see satisfactory signs and symptoms such as improvement in appetite, feeling of thirst, feeling of lightness in the body, and well-formed stool without any mucus.
2. Snehan (internal and external oleation)
Any procedure of composition that increases the availability of lubricants or generates lubrication externally or internally in the body is called “Oleation therapy”.
It is generally used as an independent therapeutic procedure for disorders of Vata and also for the preparation for Panchakarma treatment.
It is essential to perform Snehan on an individual before subjecting him to mobilize the toxic materials from their respective sites.
Snehan can be administered externally by applying medicated oil materials on the skin or internally through ingestion, enema, or nasal route.
The external application of oil is massage on the skin, the scalp, on the feet, oil as eardrops, and holding oily material in the mouth for a few minutes.
In Snehan the oily materials may be of animal (dehydrated butter, animal fat, bone marrow, fish oil) or vegetable origin (sesame oil and mustard oil).
3. Sweden (Fomentation)
Swedana or steam therapy is also known as “sudation therapy” in Ayurveda it is the process of performing sweating by a variety of methods.
It is given to liquefy oleate toxic materials that are spread throughout the body and to direct them through the alimentary canal for removal of any of the four cleaning procedures.
Swedan is given after Snehan and proceeds by Vamana (emesis therapy) in the sequence of Panchakarma treatment. Besides being the main Pre Panchakarma treatment “sudation therapy” can also be a specified treatment for a number of disorders, especially in Vata dominant. This primary treatment can be helpful in relieving stiffness, heaviness, and coldness of the body.
ii). Pradhan Karma (Main methods) which includes
- Vaman (Induced vomiting)
- Virechan (Induced purgation)
- Basti (Medicated enema)
- Nasya (Nasal medicine)
- Rakta Mokshan (Artificial bloodletting)
1. Vamana (emesis therapy)
When there is a regular attack of cough, bronchitis, colds, or asthma this particular therapeutic treatment named Vamana ( vomiting) is given to remove Kapha (congestion in the lungs).
This particular treatment is given early hours of the day until the Kapha doshas are dominant. It is performed to stabilize the vitiated doshas by removing accumulated toxins through methodically induced emesis.
Vamana Detoxification is generally suggested in diseases involving mainly Kapha doshas. The Therapy Vamana (vomiting) is also given to a person with a chronic cold, diabetes, chronic indigestion, edema, and lymphatic congestion.
2. Virechana (purgation therapy)
When excess Pitta accumulates in the liver, small intestine, and gallbladder it tends to result in acne, skin inflammation, rashes, and other ailments such as biliary vomiting, nausea, jaundice, and chronic attacks of fever.
The Ayurvedic text suggests that this condition can be administrated by therapeutic purgation. In Virechana therapy the vitiated doshas and toxins can be removed through purgation.
This therapy can be performed as a single therapy or can be followed by Vamana therapy to ensure complete detoxification. This detoxification method helps the body to expel toxins and maintain vitiated doshas from the intestines, blood, and liver.
3. Basti (enema therapy)
Vata’s Principal site is the colon generally called the large bowel or large intestine. Basti or so-called “Basti karma” is performed to remove the body’s toxins and to stabilize vitiated doshas.
It is performed by introducing medicated liquids or oils through the urethra, anus, or vaginal canal. It is generally performed by Introducing fluids and medicinal oils through the urethra in men or through the vagina in women this process is called “Uttara Basti”.
Basti therapy is the most effective treatment for the disorder of Vata. Various ailments such as arthritis, rheumatism, gout, muscle spasms, headaches abdominal distention, kidney stones, cold disorders, constipation, chronic fever, sexual, heart pain, sciatica, backache, and other pains in the joints are relieved by this therapy.
Performing Basti therapy can improve weight and nourish emaciated persons while decreasing weight in obese people.
It also improves vision, slows down the aging process, and boosts health. It is generally performed after the first two detoxification processes called Vamana and Virechana it can also be performed Virechana.
4. Nasya (errhine therapy)
The nasal administration of medication is called Nasya this detoxification method is also known as “Shirovirechana” in Ayurveda.
Ayurveda text refers to the nose as a gateway to the brain. The vitiated doshas and toxins that are accumulated in the head and neck are expelled through the nose and mouth along with nasal and oral secretions.
The atmospheric principle energy converts into life force energy known as “prana energy” It enters the body through the breath taken through the nose.
The Prana energy (breath) in the brain maintains sensory and motor functions as well as governs mental activities, concentration, memory, and intellectual activities.
The Disordered prana (breath) can create non-functioning activities and can give rise to headaches, convulsions, loss of memory, and reduced sensory perception.
So Ayurveda suggests nasal administration for prana disorders and ailments such as sinus congestion, convulsions, migraine headaches, and certain eye and ear problems can be solved.
5. Raktamokshana (therapeutic bleeding)
The accumulations of toxins material in the gastrointestinal tract are absorbed into the blood and circulate throughout the body.
When these metabolic waste products are not removed properly the free radicals produced by them may result in hypertension, a repeat of infections, and other circulatory conditions.
Other skin disorders such as hives, rashes, herpes, eczema, acne, chronic itching, or hives are also found. In such conditions “Raktamokshana” is advised.
Bloodletting procedures can be done in two ways
1. Bloodletting with Instruments:
In Ayurveda, it is called “Siravedha” bloodletting procedures can be done in various ways it can be done with the help of a needle.
Some doctors also perform veinisection but bloodletting with the needle is a very simple, safe, and easy method that can be done anywhere without any surgery.
2. Bloodletting without Instruments:
This treatment is also known as Leech application. In this treatment, a small amount of impure blood is removed from a vein to purify the Pitta.
This treatment enables the removal of toxins material and neutralizes the free radical it even cures blood-born disorders.
iii). Paschatakarma (post-detox measures) includes
Pash chat Karma: Throughout the Panchakarma treatment, a strict diet and lifestyle procedure has to be followed. The “Paschat Karma” treatment is a rehabilitation procedure to bring back the diet and lifestyle to normal.
It is a stage at which digestion power is brought back to normal. The various herbal remedy is also administered to rejuvenate the body and to treat the disease.
There is specific and different dietary regimens medicines mention in Paschata karma, it mainly consists of three procedures such as:
1) Samsarjana Krama: This specific dietary regimen is carried out to enhance dietary fire by using Peya, Vilepi, Akrita- Krita Yusha, etc. after completion of Sodhana Therapy is known as Samsarjana krama.
2) Rasyanadi Krama: When Sodhana therapy is used as Purvakarma for Rasayana and Vajeekarana after Pradhana Karma, Rasayana drug is given that is called Rasayanadi karma.
3) Samana Prayoga: When Sodhana Chikitsa is performed for a particular type of disease as part of Panchakarma treatment then a specific type of medicine is given this process is called Samana Prayoga.
All Panchakarma therapies or detoxification processes must be carried out strictly under the supervision of qualified and experienced Ayurvedic physicians.



























Very nice article…. This panchakarma therapy aims at boosting longevity in life by guiding the individual in the prevention of disease; it is efficient in cleansing of body toxins, plays a critical role in this.