What Is Ergonomics Why Is It Important?
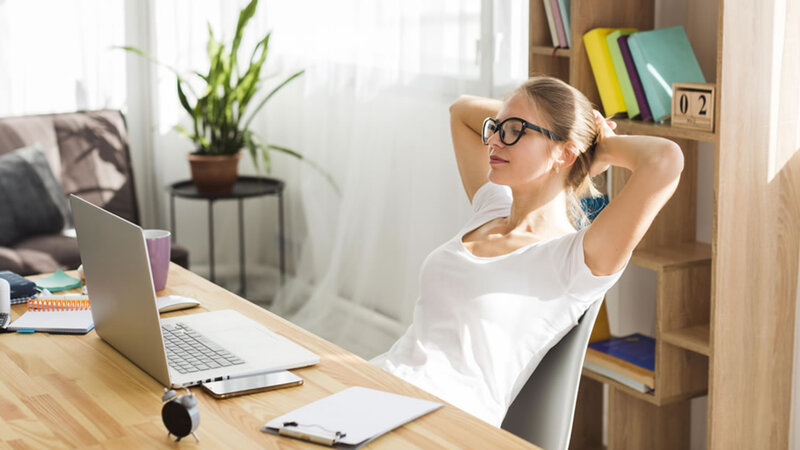 You might wonder what is Ergonomics, meaning “the study of people’s efficiency in their working environment”.You have probably heard about safety and health at work and now that we are integrating more and more into the world of teleworking and children to education from home, with much more reason.
You might wonder what is Ergonomics, meaning “the study of people’s efficiency in their working environment”.You have probably heard about safety and health at work and now that we are integrating more and more into the world of teleworking and children to education from home, with much more reason.
You may feel that there is a lot of information around this topic or that you may not know how to apply all the recommendations you hear to your life, but don’t worry anymore because here we tell you here what experts say, in a very clear way what to do in each case.
Ergonomics seeks an appropriate balance or balance between the environment that surrounds, us and the implements or equipment we use. Let’s talk about these three elements.
1. Physical space
When you think about working from home, perhaps you imagine yourself working from the sofa or bed since they are generally comfortable places or that we associate with comfortable areas of the house.
Since they are very soft surfaces, but let me tell you that although they seem comfortable, they lead to bad postures and all the more so if you wear them to work.
The recommendation will be to look for a more appropriate area such as a desk and if there is no other alternative than to work or study there, try to make it short or sporadic.
You may wonder what part of the house is the most suitable? That is a key question, choosing in advance or defining where in the house we are going to work makes a difference, and if we should share it with other family members with much more reason. It is important to find a way in which everyone can work in a well-lit and well-ventilated space.
What you should take into account
- If you do not have a desk, find a table where you can place the computer so that the gaze is in line with the screen, you can put a box or some books under the monitor.
- If you have a laptop or laptop, the recommendation is to incorporate an external keyboard to maintain alignment between your eyes, elbows, and arms.
- Find a chair that has lumbar support or put on a pillow or rolled cloth to stabilize the area and avoid recharging it.
- Another very effective option is to alternate the day and work a period of time standing and another sitting, there are specialized ergonomic sets that are very useful and practical where the computer is placed in the device so that the whole body remains aligned without reloading any area.
Our body is designed to be in movement and we must promote it!
2. Halt or breaks
Why take breaks? How often to stretch? What part of my body do I stretch? Has it happened to you that you are completely concentrated on your computer and it has been 3 hours without leaving your seat,
You have not gotten up from the chair or to go to the bathroom and from one moment to the next you begin to feel the tension in the lumbar area, buttocks, or neck that forces you to get up or change position?
If your answer is yes or if you transported yourself to that moment, let me tell you, that is your body speaking to you! Listen to it! Our body is designed to be in movement and we must encourage it, he constantly talks to us, I give you an example when we are hungry our stomach roars to tell us “go and get something to eat”.
The same happens when we stay in one position for a long time, our muscles begin to alert us through discomfort, discomfort, numbness, among others, to tell us please move!
Unfortunately, on many occasions we do not recognize when he speaks to us, we become so busy with our commitments and responsibilities that we disconnect from that communication with ourselves.
Our body is wise and begins to make compensations to maintain stability, but if these bad practices are constant, it could bill us with a very high price. This is why we recommend breaks every hour or hour and a half.
Take advantage of your phone and set alarms to remind you to take frequent breaks during your work or study hours. In these breaks, the idea is to stretch and for this listening to your body is essential as it will help you identify which area to stretch.
For example, if you feel discomfort in the lower back or gluteal area, you can start there and do stretching for that area, then in the next break – 1 hour later, you can do trunk or chest extensions and neck movements to counteract the posture.
So far forward of the shoulders that we adopt sitting in front of the computer and in another pause stretching the wrists and fingers. In this way at the end of the day, you will have stretched your entire body, activating blood circulation and oxygenation of tissues.
Another recommendation during breaks for those who work from home, in addition to stretching, is to do housework, these activities generally keep us moving.
Pauses not only have physical benefits but are also helpful in clearing the mind and renewing energy. In addition, it has been proven to increase productivity by clearing your mind and allowing you to analyze or reflect on problems and seek solutions more effectively.
3. Position
We have always been told that it is important to maintain good posture, but perhaps you have not been told that unfortunately the musculoskeletal alterations that exist today as a result of bad posture, represent one of the great causes of disability around the world! yes, it affects a lot!
We cannot ignore children, they are also suffering from alterations of this type due to the excessive use of electronic devices either for entertainment or study, so it is advisable to explain and motivate them to constantly change their position.
Here are some recommendations to maintain a good posture when you are working in front of a computer:
- Look for verticality or that the weight is on the sitting bones (little bones that we feel when we sit down) and not completely on the buttocks so as not to overload the lumbar area.
- The elbows should be positioned on the sides of the body bent at 90˚ as well as the knees also at 90˚ and with a footrest to prevent them from hanging.
- The wrists should be inside the table and not on the edge of the table or desk to avoid possible nerve compression and preferably incorporate a traditional mouse instead of the touch mouse.
We hope you can implement these recommendations in your space and way of working, so you will contribute to your health from another also important angle.