Ketogenic Diet – The Beginners Guide To Your Needs
The Ketogenic diet or so-called Keto diet is growing very popular nowadays, but most people confuse it with a low carb diet and don’t know how to really benefit from it.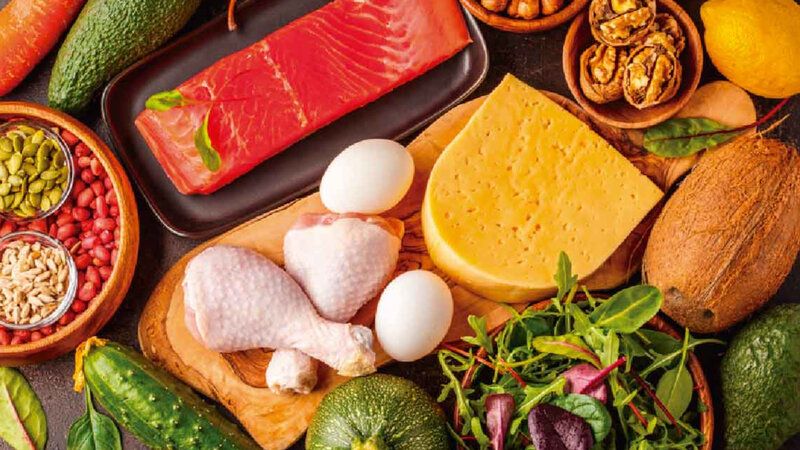
In this article, we will research the truth about the ketogenic diet, see if it is worth using and how you can make the most of it.
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a special diet originally designed in the 1920s for patients with epilepsy. Researchers at Johns Hopkins Medical Center found that fasting (avoiding any food for a short time) that helped reduce convulsions suffered by patients brought many other positive effects on adipose tissue, sugar in the blood, cholesterol, and hunger levels.
However, as you can imagine, the black post is not a viable option for more than a few days. That’s why the ketogenic diet was designed – to mimic the effects of fasting and benefit from them in the long run.
This is accomplished by minimizing foods that cause an insulinogenic response and inducing a state of physiological “ketosis. ”
What is Ketosis?
Ketosis is the name given to the state in which our body uses mainly ketone bodies to produce energy. Ketone bodies (ketones) are a certain type of molecule (acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone) that can be used as energy by most tissues, including the brain.
They are produced by the liver by breaking down fats (a process called beta-oxidation) when glucose levels are insufficient. When the levels of ketones (ketone bodies) in the blood are over 1.5 mmol/liter it is considered that we are in a state of Ketosis and we benefit to the maximum from this alternative source of energy.
Important: Ketosis should not be confused with ketoacidosis which is a serious complication of diabetes when the body produces excess ketones (or acids in the blood).
How and When to Get Ketosis?
Ketosis occurs when glucose is dramatically reduced, forcing the body to find another source of fuel: fat. Basically, ketosis can be obtained through fasting or a diet very low in carbohydrates (5% of calories or maximum 20-50g) and moderate in protein, possibly coupled with a specific physical effort that consumes glycogen stores.
Different people go into ketosis in more or less time depending on the previous lifestyle, but it generally takes 2-4 days of fasting or several days of a ketogenic diet to reach this state.
The optimal state is reached, however, only when the body remains in ketosis for at least a few weeks, when any type of side effects decrease considerably, and the benefits are much more pronounced and the body becomes a real fat burner.
Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet
1. Body Fat-Burning and Weight Reduction
Following a keto diet, burning fat, and losing weight can be very significant and rapid (especially for those who start an overweight or obese diet). A 2013 study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that:
“Those who followed a ketogenic diet achieved better long-term body weight and better management of cardiovascular risk factors compared to individuals who followed conventional diets with a low-fat content” (ie a diet with fewer calories of which less than 30% came from fat).
A summary of several studies published in the International Journal of Environmental and Public Health Research states:
“One of the most studied strategies for weight loss in recent years is the ketogenic diet. Many studies have shown that this type of nutritional approach has a solid physiological and biochemical basis and is able to induce effective weight loss along with improving several cardiovascular risk parameters. ”
In addition to changing the energy source from carbohydrates to fats, the ketogenic diet can help maintain body weight by significantly reducing hunger and cravings.
2. Maintaining Muscle Mass
Another huge advantage over most diets is maintaining muscle mass, despite consuming smaller amounts of protein. This, not only helps you look better and are more capable, but you maintain or even develop the ability of the “engine” that burns body fat.
The reason has to do with the fact that ketones reduce the need to oxidize amino acids (such as Leucine and many others) and therefore moderate amounts of protein are sufficient to maintain the required levels of amino acids in the blood.
3. High Mental Clarity
Many people who use the ketogenic diet report high concentration and more mental clarity, with some entrepreneurs using it specifically for cognitive benefits.
The reason for these benefits is believed to be the elimination of free radicals and other secondary compounds (normally resulting from the burning of glucose) when the body moves to a cleaner source of energy (ketones) and the optimization of mitochondria in brain cells.
4. Reducing the risk of Type 2 Diabetes
By significantly reducing carbohydrates and moderately protein in the diet, the ketogenic diet prevents the frequent or significant release of Insulin, leading in time to the reversal of the “Insulin resistance” of the cells that cause type 2 diabetes.
Note: Diabetics on insulin (type 1) should contact their doctor before starting a ketogenic diet as insulin doses may need to be adjusted.
5. Reducing the risk of heart disease
Despite the high amount of dietary fats, the keto diet is unlikely to have a negative impact on cholesterol levels. In fact, it is able to reduce cardiovascular risk factors, especially in obese people.
A worthwhile study found that adherence to the ketogenic food list for 24 weeks led to lower levels of triglycerides, LDL cholesterol (the “bad”) in a significant percentage of patients while increasing the level of HDL cholesterol ( The good one”).
6. Help in Cancer Prevention
Some studies suggest that ketogenic diets can “starve” cancer cells. Ordinary cells found in our body are able to use fat for energy but it is assumed that cancer cells cannot pass metabolically to the use of fats (ketone bodies) instead of glucose.
There are several medical studies such as two conducted by the Department of Oncology-Radiology at the Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center for the University of Iowa and the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke that show that ketogenic diet is an effective treatment for cancer and other serious health problems.
It is also worth mentioning that some of the best foods that fight cancer are on the list of keto diet foods.
7. Combating Brain Diseases and Neurological Disorders
Over the past century, ketogenic diets have been used to treat neurological and cognitive disorders, including epilepsy and Alzheimer’s. More recently, a study in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicated the therapeutic use of ketogenic diets for various other disorders such as headaches, neuronal trauma, Parkinson’s, sleep disorders, brain cancer, and multiple sclerosis.
The reason has to do with the fact that our brain is able to use ketones as an alternative and cleaner source of energy that induces a neuroprotective effect by correcting abnormalities in cellular energy use (common in many neurological disorders).
The ketogenic diet is also working to reverse many side effects that occur as a side effect of conventional medications for brain disorders, such as weight gain, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
8. Life Extension
There is even evidence that a low-carb, high-fat diet prolongs life compared to a low-fat, high-carb diet. In a study conducted by the American journal. The Lancet, which studied more than 135,000 adults in 18 countries, found that high carbohydrate consumption was associated with a higher risk of total mortality.
While total fats and individual types of fat were associated with lower overall mortality. Total fats and fat types were not associated with cardiovascular disease, myocardial infarction, or mortality caused by cardiovascular disease.
In fact, saturated fat intake had an inverse association with the risk of stroke, meaning that the more saturated fat a person had in their diet, the more protection they seemed to have in a stroke.
Disadvantages of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet does not seem to have any disadvantages on health, but it also comes with various challenges:
- It takes willpower for a few days or weeks until adaptation takes place and cravings for sweets and carbs are automatically reduced to a minimum.
- It restricts most foods found everywhere and can create long-term frustration because of this, it can reduce the performance of sports activities that are based mainly on glycogen as an energy source and is not ideal for muscle mass growth.
- It is difficult to eat the large according to the diet – to get both enough carbohydrates and enough healthy fats (not oxidized oils).
- It requires learning new recipes and preparing your own meals (which is not necessarily difficult) to enjoy more variety and taste.
People also ask
Who the Ketogenic Diet is for, Is it worth starting a ketogenic diet?
The answer depends on several factors. E.g:
- Do you suffer from one of the medical conditions that can treat them? Definitely worth it.
- Do you have 10 or more pounds to lose? Yes. Use it.
- Do you struggle with cravings for sweets or did most of the diets you tried not work for you? Again, yes – it’s worth using.
- Are you an active woman with a little body fat and a little appetite? Chances are it’s not a good idea for you.
- Do you want to optimize your health and body composition (fat vs. muscle) in the long run? Perfect. Try the cyclic variant.
- Do you want to grow muscle mass as fast as possible? It is also possible with a ketogenic diet, but it is not the best solution.
- Do you practice a sport that involves a lot of moderate to intense effort? Sports Performance in the ketogenic diet may suffer, especially if you exercise intensely frequently. Leisure, once or twice a week is no problem.
What You Can Eat in the Keto Diet?
Let’s see what foods allow you to eat high amounts of fat, moderate protein, and low carbohydrates. Foods Allowed in the Ketogenic Diet, Here is a list of the most used foods in the ketogenic diet:
- Meat: Fatty meats and internal organs of beef, pork, etc. – ideally from animals raised as naturally as possible.
- Fatty fish: salmon, sardines, etc.
- Eggs: It may be of different types.
- Dairy products: fatty cheeses (cheese, cheddar), sour cream, butter, ghee (clarified butter).
- Vegetables: Vegetables with low starch content: cauliflower, avocado, cabbage, broccoli, zucchini, spinach, asparagus, cucumbers, eggplant, tomatoes, olives, celery, lettuce, peppers, mushrooms, garlic, etc.
- Nuts and seeds: walnuts, almonds, macadamia, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, etc.
- Spices: salt, pepper, ginger, turmeric, cinnamon, oregano, and many more
- Oils: extra virgin olive, coconut, avocado, almond, etc.
- Fruits: Avocado
Important: The proportions of macronutrients matter a lot!
Eating the foods from the list above is not enough. If you want to follow a ketogenic diet in the true sense of the word and benefit from its advantages, you must make sure that you reach certain amounts of protein, carbohydrates, and fats.
Forbidden Foods in the Keto Diet
Here is a list of foods that could easily get you out of ketosis and therefore should be limited or completely removed from your daily meals:
- Sugar in all its forms, including natural sugars such as raw honey or maple syrup
- All types of cereals, grains, and flour products. This includes oats, rice, quinoa, corn, bread, and all bakery products.
- Fruits, with few exceptions such as berries, avocados, etc.
- All carbohydrate-rich vegetables such as potatoes, corn, beans, peas, lentils, etc.
- Caloric drinks, including alcohol and milk.
- Virtually all foods that will bring you more carbohydrates than your daily recommendations.
Note: “Forbidden” is a bit exaggerated.
It all depends on the quantities
For example, a tall, muscular man could consume as much as 50gm of carbohydrates a day without getting out of ketosis. Therefore, you could add a fruit or yogurt a day without exceeding the limit, even if you eat healthy with a lot of recommended foods such as various vegetables and greens, avocados, and others that already contain few carbohydrates.
However, carbohydrates with a high glycemic index would be better avoided, and if you are not sure about the amounts or simply do not want to bother with the calculations, it is best to consider all the above foods as “forbidden”.
How Much Can You Eat in the Ketogenic Diet?
In a standard ketogenic diet (sometimes called “strict”) you need to achieve the following proportions of macronutrients:
- Protein: 15-20% of Calories
- Carbohydrates: 5% Calories
- Fats: 75-80% of Calories
Here is an example calculation:
Step 1: Use an online computer to estimate your daily calorie target. You enter your age, height, weight, activity level, and goal (weight loss) and it will make the recommendation for you.
Let’s say it’s 2800 Calories.
Step 2: Calculate the amounts of macronutrients you need.
Calorie Protein = 15% x 2800 = 420
Calories from Carbohydrates = 5% x 2800 = 140
Calories in Fat = 80% x 2800 = 2240
Knowing the calories per gram of macronutrient, we can easily calculate the number of grams:
Grams of Protein = Calories from Protein / 4 Calories per gram = 420/4 = 105
Grams of Carbohydrates = Calories from Carbohydrates / 4 Calories per gram = 140/4 = 35
Grams of Fat = Calories in Fat / 9 Calories per gram = 2240/9 = 249
Step 3: Think about how you divide them throughout the day and make sure you get them from the foods you eat. For this you will need to know how many grams of protein, carbohydrates, and fats are found in everything you eat, to gather and adjust them, or follow a ready-made plan for your caloric needs.
Whichever method you choose, it is extremely important to reach these proportions. Just as you will not get into ketosis by eating more carbohydrates or overdoing it with protein, it is not better if you eat less fat!
Only at these amounts and proportions, you will really benefit from the advantages of the diet.
Long Term Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet is one of the few nutritional diets that can bring enormous long-term health benefits. (Obviously, as long as you eat quality food and take into account the rest of the healthy nutritional practices, not just the proportions of macronutrients).
However, today most doctors and experts in the field recommend cyclic exit and re-entry into the state of ketosis after the initial period of several weeks of adaptation to the ketogenic diet.
How often you eat a ketogenic diet and how often you add carbohydrates (ideally from healthier sources such as fruits, rice, potatoes, etc.) depends on your needs and priorities. It can be 1-2 days a week if you train often and intensely or it can be 1 day every 10-14 weeks if you have a predominantly sedentary lifestyle.
“Supreme” Diet for Optimal Weight Loss
If you are tempted to follow a ketogenic diet (a few extra tricks) to lose weight as quickly as possible, minimizing the chances of regaining fat. The solution present to you is to study detailed nutritional plans step by step, automatically calculated for your body’s needs, which are based on a ketogenic diet and other last-minute strategies to get rid of unwanted fat as quickly as possible.























hey there and thank you for your info ? I?’ve definitely picked up something new from right here