The Best Panchakarma Therapies to Try in Kerala
Kerala, renowned for its rich Ayurvedic heritage, offers some of the most effective Panchakarma therapies designed to rejuvenate and restore balance to the body and mind. The best Panchakarma treatments in Kerala include a range of detoxification and therapeutic practices.
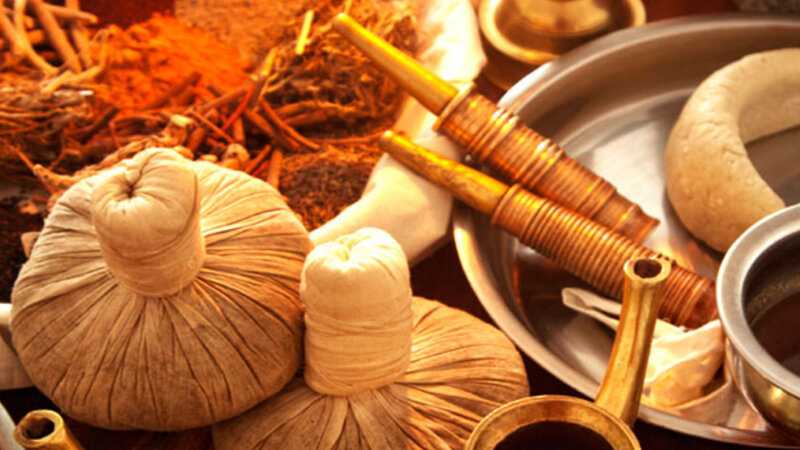 Such as Abhyanga (therapeutic oil massage), Vamana (therapeutic vomiting), Virechana (purgation), Basti (medicinal enemas), and Nasya (nasal administration).
Such as Abhyanga (therapeutic oil massage), Vamana (therapeutic vomiting), Virechana (purgation), Basti (medicinal enemas), and Nasya (nasal administration).
These treatments are administered at top Ayurvedic centers across Kerala, where experienced practitioners use traditional methods and high-quality natural ingredients to address various health conditions, from chronic ailments to stress. Each therapy is tailored to individual needs, ensuring a holistic approach that promotes overall wellness and vitality.
What is Shamana Therapy?
The palliation process (Shamana), is the treatment to eliminate the most serious toxins. Palliation consists of neutralizing toxins by igniting Agni and stimulating digestion through fasting.
Toxins can also be neutralized through the internal use of hot and spicy herbs like ginger and black pepper. Hunger and thirst, exercise, sunbathing, and fresh air are other means of neutralizing toxins.
What Are the Five Actions of Panchakarma?
People new to ayurvedic massage generally have questions, What is included in panchakarma? it is a body purification treatment of Ayurveda.
It consists of five (‘Pancha’) cleansing actions (‘karma’). The five basic processes are vomiting, purgatives or laxatives, medicinal enemas, nasal administration of medicines, and purification of the blood, whose names in Sanskrit are:
- Nasya (oil-based nasal cleansing or medicated herbal powders)
- Vamana (controlled vomiting)
- Virechana (digestive system purge)
- Basti (enema or colon irrigation)
- Bleeding (or blood-letting)
The truth is, some cleanings sound a lot worse than they actually are. We are going to explain each one of them. It is important to remember that these techniques must be practiced by prescription and under the supervision of a specialist:
1. Nasya Panchakarma
Nasya is a specialized Ayurvedic treatment involving the nasal administration of medicines. This process is designed to eliminate excess doshas that have accumulated in the throat, nose, sinuses, or head. Nasya is based on the principle that the nose serves as a vital gateway to the brain and consciousness, and through it, the vital energy or prana enters the body.
Purpose and Benefits of Nasya:
- Eliminating Doshas: Nasya aims to clear excess doshas (imbalances in the body’s energies) from the upper respiratory tract and head region.
- Restoring Prana: By correcting prana (vital energy) imbalances, Nasya helps address disorders affecting sensory functions, brain health, and overall vitality.
- Addressing Conditions: It is commonly used for a range of issues including dry nasal passages, sinus congestion, hoarseness, migraines, seizures, and certain eye and ear problems.
Guidelines for Nasya Administration:
- Timing: Nasya should not be administered immediately after bathing, eating, sexual activity, or alcohol consumption. It is also advised to avoid Nasya during pregnancy and menstruation.
- Technique: For nasal administration, a few drops of medicated oil or powder are introduced into the nostrils. This treatment helps in clearing blockages and balancing doshas.
Additional Practices:
- Nasal Massage: To improve breathing and enhance the effectiveness of Nasya, a gentle nasal massage can be performed. This involves applying ghee to the little finger and slowly massaging the inner walls of the nose. This technique can help release stored emotions and promote a sense of well-being.
Role in Detoxification:
Nasya is also part of the broader detoxification process in Ayurveda. Toxins absorbed through the digestive system can circulate through the body, manifesting as various health issues. Nasya helps in eliminating these toxins from the nasal passages and can aid in the overall purification of the body.
2. Vamana Panchakarma
Vamana Panchakarma is an Ayurvedic therapeutic process involving induced vomiting, primarily used to address conditions related to excess Kapha dosha. This treatment is effective for a variety of ailments associated with congestion in the lungs and respiratory system.
Purpose and Benefits of Vamana Panchakarma:
- Kapha Imbalance: Vamana aims to eliminate excess Kapha, which is associated with mucus production and congestion. This imbalance can lead to conditions such as bronchitis, asthma, chronic cough, and cold.
- Additional Indications: The treatment is also beneficial for various other conditions including skin diseases, chronic asthma, diabetes, chronic catarrh, lymphatic obstruction, chronic indigestion, edema (swelling), epilepsy (to be performed between seizures), chronic sinus issues, and frequent angina.
Procedure:
- Preparation:
- Begin by consuming three to four glasses of licorice or calamus root tea milk. These substances help prepare the body for the vomiting process.
- Alternatively, in the morning before brushing your teeth, drink two glasses of water with added salt. This helps to aggravate the Kapha dosha and prepares the body for the subsequent vomiting process.
- Induction of Vomiting:
- The process involves rubbing the back of the tongue to induce vomiting. This action helps in expelling the accumulated mucus and can also assist in releasing emotional blockages.
- The aim is to expel the excess mucus and toxins from the stomach and respiratory system.
- Post-Vomiting Relief:
- Once the mucus is expelled, patients often experience immediate relief from symptoms. The treatment helps clear congestion, alleviates suffocation and shortness of breath, and clears the sinuses.
Benefits:
- Clearing Mucus: Vamana effectively clears mucus and alleviates symptoms associated with Kapha imbalances.
- Improved Respiratory Health: Relief from congestion and breathing difficulties is often noted following the treatment.
- Overall Well-being: The process can help in reducing symptoms of various chronic conditions and improving general health.
Cautions:
- Supervision: Vamana Panchakarma should be performed under the supervision of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner, as it involves inducing vomiting which requires careful management.
- Contraindications: This treatment may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain health conditions or during specific periods such as pregnancy.
3. Virechana Panchakarma
Virechana Panchakarma is an important Ayurvedic detoxification treatment aimed at addressing conditions caused by excessive bile secretion and accumulation. This therapy involves the use of purgatives or laxatives to cleanse the body, particularly targeting the liver, gallbladder, and intestines.
Purpose and Benefits of Virechana Panchakarma:
- Bile Accumulation: Excess bile in the gallbladder, liver, and intestines can lead to various health issues, including skin inflammations, allergic skin eruptions like acne or dermatitis, chronic fever, ascites (fluid retention in the abdominal cavity), bile vomiting, and jaundice.
- Detoxification: Virechana aims to eliminate excess bile and toxins from the body, thereby improving skin health and alleviating digestive and liver-related issues.
Procedure and Methods:
- Use of Purgatives:
- Senna Leaves: Infusions of senna leaves are a commonly used mild laxative. However, it may cause discomfort in individuals with a Vata constitution due to its strong effects on the large intestine’s peristaltic movements.
- Ghee and Warm Milk: For individuals with Vata and Pitta constitutions, a glass of warm milk mixed with two teaspoons of ghee can be an effective laxative. This remedy is typically taken before bedtime to alleviate disorders associated with excess Pitta, such as excessive bile production. This method can also help balance Pitta and provide a soothing effect.
- Diet Considerations:
- Pre-Treatment Diet: Before administering purgatives, it’s crucial to assess the patient’s diet. An imbalanced diet can aggravate symptoms and hinder the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Avoiding Certain Foods: Ensuring the patient follows a balanced diet is key to preventing further imbalances.
Cautions and Contraindications:
- Low Agni (Digestive Fire): Purgatives should not be used if the patient has low digestive fire (Agni), as this can lead to adverse effects such as fever, diarrhea, constipation, or even rectal bleeding.
- Conditions to Avoid: Avoid administering Virechana in cases of external tumors in the stomach, immediately following an enema, or in situations of wasting, weakness, or rectal prolapse.
Benefits of Virechana Panchakarma:
- Cleansing: The therapy effectively cleanses the liver and intestines, helping to eliminate excess bile and toxins.
- Relief from Symptoms: Patients often experience relief from skin issues, digestive disorders, and jaundice after undergoing Virechana.
- Balanced Doshas: By removing excess bile, Virechana helps balance the Pitta dosha, which can be particularly beneficial for those with Pitta imbalances.
4. Basti Panchakarma
Basti Panchakarma is a traditional Ayurvedic treatment that involves the administration of medicinal enemas. This therapy is particularly effective for managing disorders associated with Vata dosha, which is linked to a range of conditions due to its dry, mobile, and irregular qualities.
Purpose and Benefits of Basti Panchakarma:
- Vata Disorders: Basti is designed to address various Vata imbalances, which can lead to conditions such as constipation, bloating, chronic fever, common colds, sexual disorders, kidney stones, vomiting, back and neck pain, and hyperacidity.
- Comprehensive Treatment: This therapy is beneficial for a wide range of diseases associated with Vata dosha, including sciatica, arthritis, rheumatism, and gout. Given that Vata dosha plays a significant role in numerous pathologies, Basti offers a holistic approach to managing these conditions.
Procedure and Methods:
- Administration of Enemas:
- Types of Substances: Medicinal enemas may include substances such as sesame oil, calamus root oil, or decoctions of various herbs. These substances are introduced into the rectum to provide therapeutic benefits.
- Purpose of Oils: Oils like sesame oil are used to lubricate and soothe the rectal and intestinal tissues, which helps in alleviating symptoms associated with Vata imbalances.
- Indications:
- Constipation and Bloating: Basti helps in relieving constipation and bloating by improving bowel movements and easing discomfort.
- Vata-Related Conditions: It is effective in treating conditions exacerbated by Vata dosha, such as arthritis and sciatica.
Contraindications and Cautions:
- Diarrhea and Rectal Bleeding: Basti should not be administered if the patient has diarrhea or is experiencing rectal bleeding, as it could exacerbate these conditions.
- Chronic Indigestion and Other Conditions: Oil enemas are generally avoided in individuals with chronic indigestion, cough, suffocation, diarrhea, diabetes, or severe anemia. It is also not recommended for the elderly or children under seven years of age.
- Consultation: Due to the specific nature of the treatment, it is essential to have a thorough assessment by an Ayurvedic practitioner before proceeding with Basti.
Benefits of Basti Panchakarma:
- Relief from Vata Disorders: Basti provides significant relief from conditions related to Vata dosha, improving overall well-being.
- Comprehensive Care: It addresses a wide range of symptoms and conditions, offering a complete therapeutic approach to Vata-related health issues.
- Restoration of Balance: By alleviating excess Vata, Basti helps restore balance to the body’s energies and supports overall health.
5. Bloodletting (or blood-letting)
Bloodletting, known as Raktamokshana in Ayurveda, is a therapeutic practice aimed at removing a small amount of blood from the body to treat certain health conditions. This procedure is particularly effective for managing diseases associated with excess Pitta dosha, where toxins and impurities are believed to accumulate in the blood.
Indications for Bloodletting:
- Skin Diseases: It is often indicated for frequent attacks of skin conditions such as rashes, acne, and other inflammatory skin disorders where toxins are present in the blood.
- Hepatomegaly and Splenomegaly: Bloodletting can help alleviate symptoms related to enlarged liver (hepatomegaly) and spleen (splenomegaly).
- Gout: This practice is used to manage gout, a condition characterized by painful joint inflammation due to excess uric acid.
Mechanism and Benefits:
- Toxin Removal: By drawing a small amount of blood, bloodletting helps remove toxins and impurities that have accumulated, thus relieving the tension created by these toxins.
- Stimulation of Anti-Toxic Substances: The procedure can stimulate the production of anti-toxic substances in the blood, strengthening the body’s immune response and aiding in detoxification.
- Blood and Bone Health: The removal of toxins through bloodletting can contribute to the radical cure of diseases related to blood and bones.
Procedure:
- Method: Bloodletting involves drawing a small amount of blood from the veins, typically through a controlled and sterile procedure. The exact method and quantity depend on the individual’s condition and needs.
Contraindications:
- Anemia: Bloodletting is contraindicated in individuals with anemia, as it can exacerbate their condition by further reducing blood volume.
- Edema and Weakness: It is not recommended for those with edema (fluid retention) or general weakness, as the procedure may worsen these conditions.
- Children and Elderly: The treatment is generally avoided in children and the elderly due to their increased vulnerability and differing physiological responses.
Post-Treatment and Dietary Considerations:
- Dietary Precautions: Post-bloodletting, it is advisable to avoid excess sugar, salt, yogurt, and certain sour foods, as these can be toxic to the blood and counteract the benefits of the treatment.
- Blood Purifying Herbs: After the procedure, herbs and substances that support blood purification can be beneficial. Some recommended options include:
- Burdock Root (Artium lappa): Known for its blood-purifying properties.
- Saffron, Sandalwood Powder, Turmeric: These herbs help in detoxifying and purifying the blood.
- Calamus Root (Acorus calamus): Another herb useful for blood purification.
- Red Pomegranate Juice, Orange Juice, Asparagus Root: These also aid in cleansing and supporting blood health.
Panchakarma is a comprehensive Ayurvedic detoxification and rejuvenation therapy designed to restore balance and promote overall well-being. The five primary actions of Panchakarma—Vamana, Virechana, Basti, Nasya, and Raktamokshana—each serve a specific purpose in addressing various imbalances and health conditions.